
interface Tunnel3 Tunnel3 uses TE metric (default)for path selection ip unnumbered loopback0 tunnel destination 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.0 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel mpls traffic-eng. You will get a comprehensive overview of all the aspects of MPLS, including the building blocks, its applications, troubleshooting and a perspective on the future of MPLS. tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-selection-metric igp Use IGP cost for path selection. P-routers P1 and P2 swap outer IGP label and forward label packet to PE1. This book also reviews the different MPLS applications (MPLS VPN, MPLS Traffic Engineering, Carrying IPv6 over MPLS, AToM, VPLS, MPLS OAM Explain the Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) extensions used to build the Traffic Engineering. This book focuses on the building blocks of MPLS (architecture, forwarding packets, LDP, MPLS and QoS, CEF, etc.). Describe the default Junos OS MPLS traffic engineering behavior. EoMPLS, VPWS, VPLS, EVPN, and much different data plane with it is covered.
The course continues with Intra AS MPLS VPN for Layer 2 and Layer 3 VPNs. MPLS Control plane and MPLS Data plane basics are explained. MPLS has grown to be the new default network layer for service providers and is finding its way into enterprise networks as well. In this MPLS VPN Zero to Hero Training, MPLS Fundamentals is explained as a first topic. For many service providers and enterprises MPLS is a way of delivering new applications on their IP networks, while consolidating data and voice networks. MPLS has emerged as the new networking layer for service providers throughout the world.
#Mpls fundamentals igp series
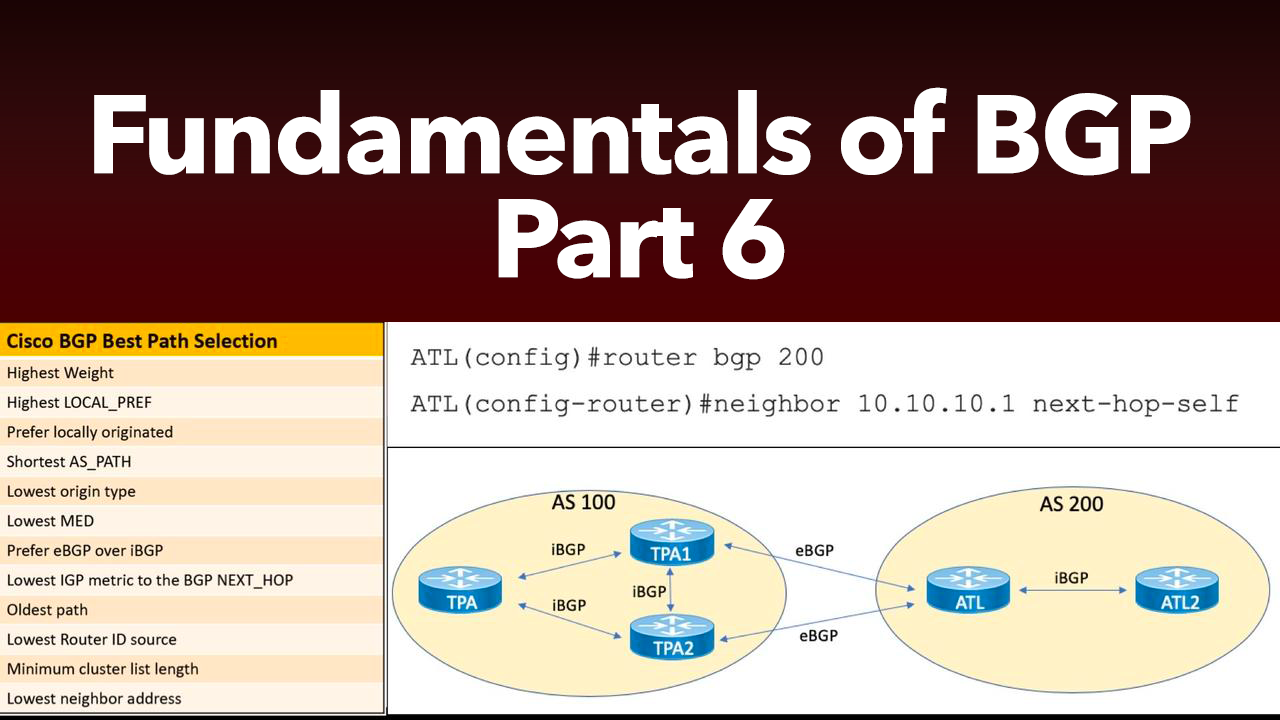
The Fundamentals Series from Cisco Press launches the basis to readers for understanding the purpose, application, and management of technologies After introducing concepts such as MPLS forwarding and the structure of the MPLS header, the course will delve into the configuration and operation of the two main label distribution protocols, RSVP and LDP. VRFs solve the problem of overlapping IP prefixes, and provide the required. Unlike BGP VPLS, which is OSI Layer 2 technology, BGP VRF VPNs work in Layer 3 and as such exchange IP prefixes between routers. Provides MPLS theory and relates to basic IOS configuration examples This two-day course is designed to provide students with a solid foundation on Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS). RouterOS 3.x allows to create multiple Virtual Routing and Forwarding instances on a single router. Synchronization means that the packet forwarding out of an interface - Selection from MPLS Fundamentals. Resolution Example - Route Resolution Summary - IGP Passive Versus Next-Hop Self for BGP.

BGP for SR-MPLS is an extension of BGP for Segment Routing. However, IGP for SR-MPLS does not work if paths cross multiple ASs on a large-scale network. Proper SID orchestration in an AS facilitates the planning of an optimal path in the AS. Helps networking professionals choose the suitable MPLS application and design for their network the IGP of the network are not synchronized. TOPICS - MPLS Fundamentals - MPLS Foundation Terminology - MPLS. IGP for SR-MPLS allocates SIDs only within an autonomous system (AS). A comprehensive introduction to all facets of MPLS theory and practice


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
